Melting glass is an expensive and energy-intensive process. Some 35% of glass manufacturing costs are accounted for by the energy used, and requirements relating to the refractory materials of the melting units are high so as to restrict their corrosion by the aggressive melt.
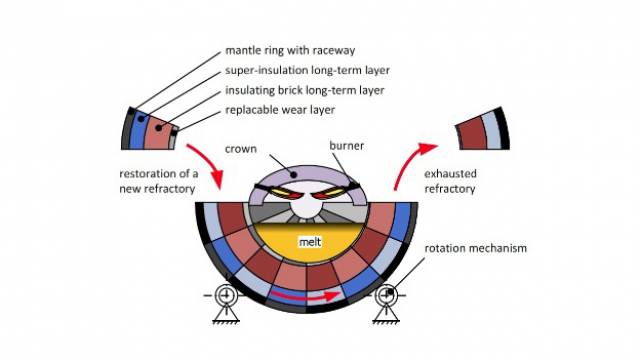
Dynamic Furnace GmbH has developed an alternative melting process for the glass industry that can significantly reduce material and energy costs. The key innovation lies in being able to replace damaged and corroded refractory components on an ongoing basis without interrupting the melting process. This eliminates maintenance work and subsequent firing up of the plant. This ongoing replacement of corroded components makes it possible to save on costs by using far more economical refractory materials. Since corrosion of refractory components no longer limits the furnace’s service life, cooling is superfluous and the entire melting plant can be insulated. Taken together, these factors reduce energy requirements by up to 15% and manufacturing costs by an estimated 7%.
Dynamic Furnace has completely redesigned the tank, its bearing system and the control system. A special mechanism enables the semi-circular tank to rotate slowly but continuously in one direction during operation. This exposes corroded or damaged components on one side of the surrounding wall. It is then quick and easy to remove them, while new bricks are inserted on the opposite side.
Dynamic Furnace GmbH will be unveiling this new technology to the trade public at this year’s glasstec 2014 at the joint stand of the Deutsche Glastechnische Gesellschaft and Hüttentechnische Vereinigung der Deutschen Glasindustrie (HVG-DGG).